Introduction
Elbow fracture occurs where one of the bones in the elbow joint breaks – this includes breaks in the bone of the upper arm (the humerus), the outside bone in the forearm (the radius) or the inside bone in the forearm (the ulna). Elbow fracture is particularly common in children, in fact it is the most common type of bone fracture in children, happening most frequently in children aged 5-8.
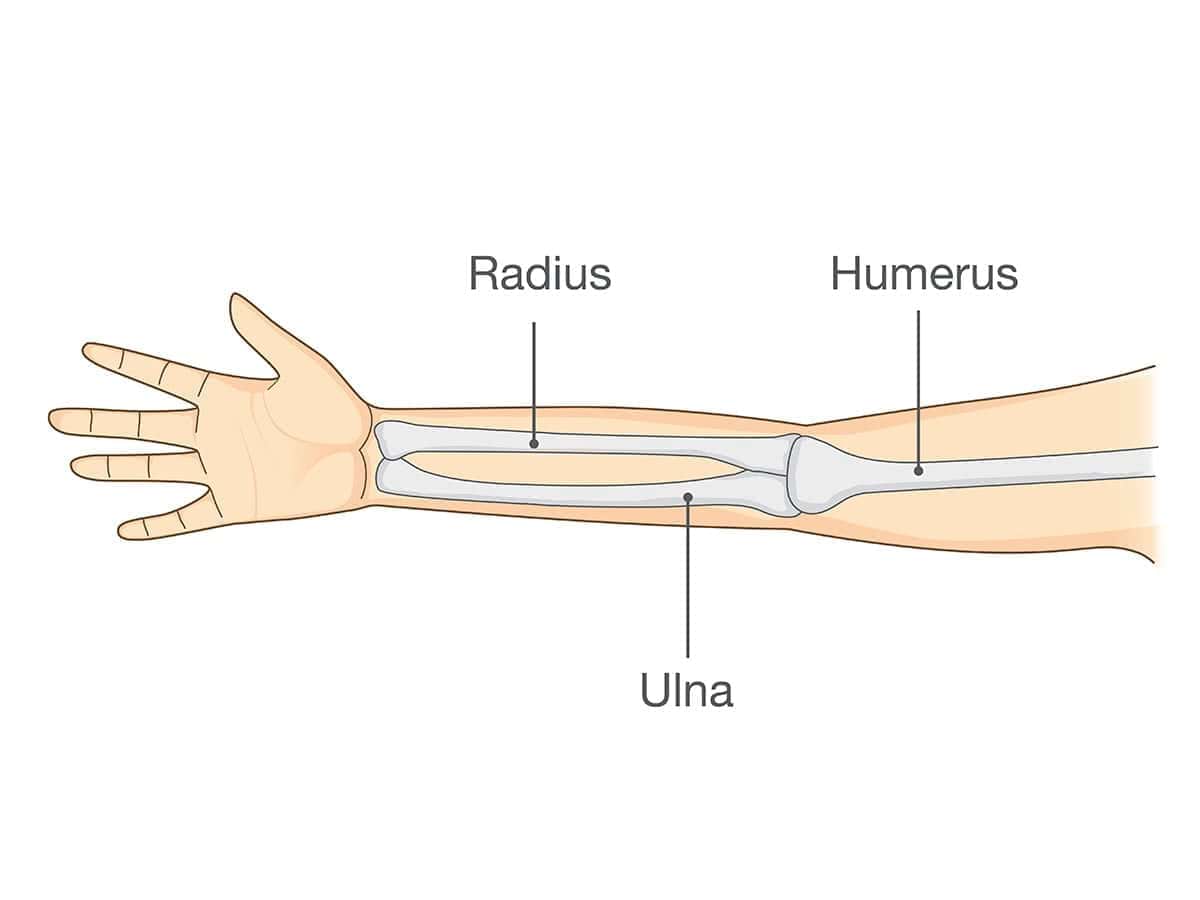
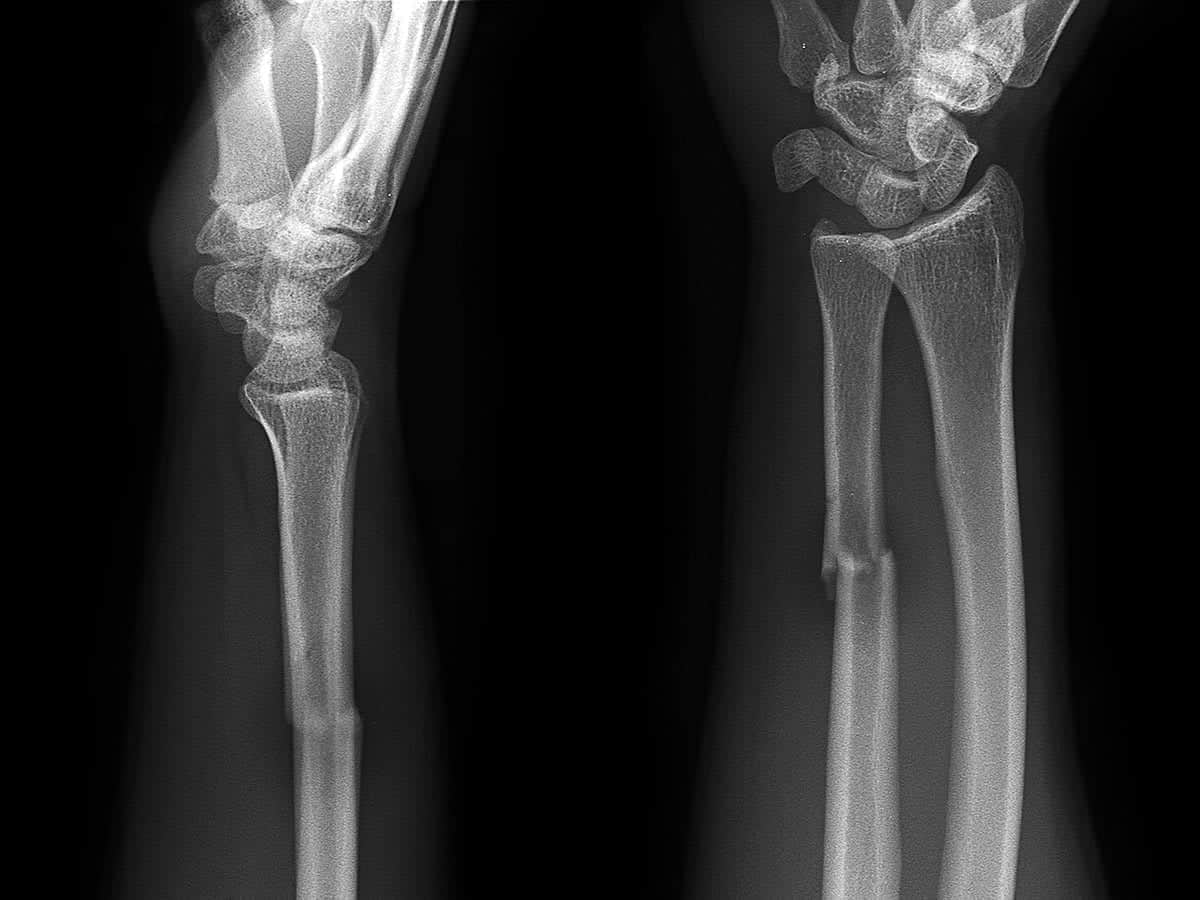
Causes
Elbow fractures are generally caused by:
- Trauma / impact (such as a direct blow to the elbow).
- Falling on an outstretched hand ('FOOSH') especially where the elbow is exposed.
- A severe twisting of the elbow.
Symptoms
- Pain (generally quite severe).
- Noticeable deformity of the elbow.
- Inability to bend the elbow.
- Bruising / swelling of the elbow.
- Tenderness / stiffness.
- Numbing of forearm / hand / fingers (indicating possible nerve damage).
- Cracking / popping sound when moving the elbow.
Tests / Diagnosis
Most people with these symptoms are required to have an immediate x-ray to determine the extent of the damage.
Treatment
Treatment depends entirely on the nature of the fracture/s. If the fracture has not moved out of position, surgery may not be required. In more complex cases (e.g. Where there are multiple fractures, or the fractures have moved out of position) surgery is generally required.

